Dr. Muhammad Mustehsan Bashir
MCPS (surgery); FCPS (Surgery); FCPS (Plastic Surgery)
Professor & CHairman
Email: mmbashir1@gmail.com
INTRODUCTION OF DEPARTMENT
With Faith, Discipline, and Selfless Devotion to Duty, There Is Nothing Worthwhile That You Cannot Achieve – Quaid-e-Azam –
Founded in 1987 as a 6 bedded facility in an unnoticeable nook of the Chest Surgery ward, the Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, King Edward Medical University today comprises of 94 beds and is the largest of its kind in Punjab. With a well equipped 25 bedded burn centre HDU and 5 bedded burn ICU, it is one of the best burn centers in the country. With the legendary Professor Abdul Hakim Babar as its pioneer, the department began galvanizing to greater heights commensurate with international standards under the aegis of his protégé and successor, Professor Farid Ahmad Khan. Currently headed by the dynamic
Prof. Dr. Mustehsan Bashir, the department has fully acclimatized itself to the recent trends in our rapidly evolving specialty. Equipped with the latest machinery, all state of the art procedures are being performed in the unit including reconstructive, cosmetic, microvascular and trauma surgery. The department takes emergency as well as elective referrals not only from Punjab but from the whole country. Today the department caters to a staggering average of 16320 patients annually and operates on 2544 patients yearly.
GOALS AND OBJECTIVES
Excellence is not a skill. It is an attitude.
All efforts are made in our department to strive for the highest standards in patient care, resident training and discipline as well as instilling ethics and a positive attitude amongst our staff. Complacence is the enemy of excellence, so we continue to arm ourselves with the latest equipment allowing us to operate in line with the recent advances in our field. Relevant machinery has been procured to offer not only better reconstructive but also cheap and reliable cosmetic surgery to the common man. We intend to provide specialized patient care and it is our aim to delineate the scope of Plastic Surgery procedures to the medical community for appropriate referrals and better patient management. It is due to the diligent efforts of the faculty and residents that emergency facial and upper limb surgery including limb replants are being performed on a regular basis.
FACULTY

| Sr. No. | Name | Designation | Qualification | Contact Information |
| 01 | Prof. Dr Muhammad Mustehsan Bashir | Professor | FCPS(Surgery); FCPS (Plastic Surgery) | mmbashir1@gmail.com |
| 02 | Dr Hamid Hussain Ansari | Assistant Professor | FCPS (Plastic Surgery) | dhamidansari@yahoo.com |
| 03 | Dr Muhammad Sohail | Assistant Professor | FCPS (Surgery); FCPS (Plastic Surgery) | drsohail72@gmail.com |
| 04 | Dr Saadia Nosheen Jan | Assistant Professor | FRCS (Ed); FCPS (Plastic Surgery) | saadia_jan@yahoo.com |
| 05 | Dr Afzaal Bashir Bajwa | Assistant Professor | FCPS (Plastic Surgery) | dr.afzaal@yahoo.com |
| 06 | Dr Lubna Cheema | Assistant Professor | FCPS (Surgery) | drlubnacheema@gmail.com |
EDUCATIONAL ACTIVITIES
- Courses: FCPS , MS (Plastic Surgery )
- Weekly journal club (Research paper presentation)
- Exam preparation courses (long and short case presentation)
- Monthly morbidity and mortality meetings on every second Friday.
- Interdepartmental meetings held on every month.
- Burn symposium
- Workshops on research methodology, synopsis writing, communication skills and IT (Information Technology).
RESEARCH
Our staff members regularly attend conferences and present research papers in conferences, workshops and symposiums. The Department itself conducts conferences on Burns, flap harvesting and Plastic Surgery in general. Special emphasis is laid on the training of residents. Weekly presentations, journal clubs and tests are held to make sure they meet the required standards. An internal evaluation Performa is circulated among the faculty members every 2 months to evaluate the residents and focus on their shortcomings individually. The unit is accredited for a 3 year FCPS training program and a 5 year MS in Plastic Surgery course. An onsite reading room is available for the convenience of our residents. Our aim is to produce competent, ethical and confident fellows who are both safe and sagacious decision makers and surgeons. Apart from teaching post graduate residents, the unit is also actively engaged in the teaching of MBBS and physiotherapy students who rotate in the department on a monthly basis apart from attending weekly lectures.
- Supraclavicular artery flap: its role in reconstructing post burn neck contractures: Annals of KEMU; Vol 13 Issue 1; Jan-March 2007
Interesting etiology of Burns: Journal of Fatima Jinnah Medical College Apr 2008 2(2); 57-9 - Determinants of wound Dehisence in Abdominal Surgery in Public Sector. Annals of KEMU. Vol 14 no 3; July-Sept 2008
- Sural Artery Flap: its role in reconstructing heel defects: Journal of PAPS
- Comparison of traditional two injections dorsal digital block with volar block . JCPSP 2009;Vol18(12); 768-70 Impact Factor
- Comparison of ambulatory and in-patient cleft lip surgery in adults. JAMC,,2010
- Comparison of suture and graft techniques in unilateral cleft rhinoplasty; Journal of Craniofacial Surgery; Nov 2011 Impact Factor
- Xeroderma Pigmentosum; A 7 year experience; JCPSP Feb 2011 Impact Factor
- Comparison of wet normal saline and honey dressing in wound preparation for skin grafting. Annals of KEMU 2011Vol 18(12) 68-77
- Factors associated with post piercing auricular cartilage keloids. JCPSP 2011;21(10)606-610 Impact Factor
- Reducing the notch in primary cleft lip repairs; comparison of Noordhoff triangular flap with Z plasty. JCPSP May 2012; Vol. 22 (5): 307-310 Impact Factor
- Salvage of infected tissue expander: Journal of PAPS 2013
- Outcome of modified turn down flaps for the lining with primary cartilage grafts in nasal reconstruction: Journal of Craniofacial Surgery Feb 2013 Impact Factor
- Flexor zone 5 cut injuries: emergency management and outcome: JCPSP March 2014 Impact Factor
- The outcome of microvascular free flap surgery with or without use of post operative heparin: JCPSP May 2014 Vol 24(6);412-15 Impact Factor
- Comparison of bupivacaine soaked dressing and conventional dressing for pain relief at split thickness skin graft on donor site. JCPSP June 2014 Vol 24-6;416-419 Impact Factor
- Comparison of post operative pain relief with intercostal block between pre rib harvest and post rib harvest groups; JCPSP 2014Vol 24(1); 43-46 Impact Factor
- Intralesional triamcilone alone and in combination with 5-FU for the treatment of keloid and hypertrophic scars: accepted JPMA Sep 2014 vol 64 Impact Factor
- Use of commercial markers (stationary grade) versus sterile markers for per âoperative marking: a comparison study. Annals of KEMU; Jan-March 2015. Vol 21(1) 44-47
- Microbiological patterns of burn wound cultures at Mayo Hospital Lahore Burn Unit. Annals of KEMU; Apr- June 2015;Vol 21(2); 67-73
- Comparison of single intra operative versus an intra operative and two post operative injections of triamcinolone after wedge excision of keloids of helix. JPMA July 2015; 65: 737; 2015 Impact Factor
- Diagnostic accuracty of blood glucose measurements in detecting venous compromise in Flaps. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery 2015 Jul;26(5):1492-4 Impact Factor
- Effect of time interval between Tumescent Local Anaesthesia Infiltration and Start of Surgery on Operative Field Visibility in Hand Surgery without Tourniquet. J Hand Surg Am. 2015 Aug; 40(8):1606-9. Impact Factor
- Outcome of management of vascular malformations of lip Published in Journal of Craniofacial Surgery September 2016 (Impact Factor)
- Comparison of clinical outcome of FAMM (Facial Artery Myomucosal) flap and Tongue flap for closure of large anterior palatal fistulas.
- Published in Journal of Craniofacial Surgery September 2016 (Impact Factor)
- A Modified Suction-Assisted Technique of Transfer of Diced Cartilage Graft to Carrier Material and Outcome of Direct Injection of Unwrapped Diced Cartilage in Rhinoplasty. Published in Journal of Craniofacial Surgery June 2017 (Impact Factor)
- Outcome of Coverage of Post Burn Palmar Hand Contractures with Glabrous Intermediate-Thickness Plantar (ITP) Skin Graft VOL 23 NO 3 (2017): AKEMU
- Traumatic Wounds of the Upper Extremity: Coverage Strategies Hand Clinics Volume 34, Issue 1, February 2018, Pages 61â74 (Impact Factor)
- Outcome of conventional adipose tissue grafting for contour deformities of face and role of ex-vivo expanded stem cells (ASCs) in treatment of such deformities. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery, 2018 Feb 23 (Impact Factor)
- Comparison of Laser Doppler Imaging (LDI) and clinical assessment in differentiating between superficial and deep partial thickness burn wounds. Accepted for publication in Burns Journal 2018 Mar;44(2):405-413.
- Outcomes of post burn flexion contracture release under tourniquet versus tumescent technique in children Accepted for publication in Burns Journal (Impact Factor) May 2018 Volume 44, Issue 3, Pages 678â682.
- To compare the cosmetic outcome of dermabond tissue and conventional suture in unilateral congenital cleft lip.(accepted of publication)
- Comparative study of topical conventional and topical heparin treatment in second degree burn patients for analgesia and duration of wound healing.(accepted of publication)
Ongoing research projects:
Completed Studies:
- Sensory recovery of Reverse Homodigital Island Flap in Finger tip reconstruction.
- Comparison of propranolol with prednisolone in the treatment of infantile haemangioma.
- Potential of mesenchymal stem cells enriched fat grafting for contour deformities of face.
CURRENT PROJECTS:
- Long term effects on skin hyper pigmentation after mesenchymal stem cell enriched adipose tissue grafting for contour deformities of face with pigmentary changesâ.
- Outcomes comparison of superficial partial thickness burn (as confirmed by laser doppler) on the faceâ.
- Functional and Aesthetic outcomes of Debulking through one-stage, two stage surgical Debulking and Suction-assisted Lipectomy in Fasciocutaneous flapsâ.
- Post operative patient satisfaction and anthropometric analysis in Rhinoplastyâ.
- Comparison of Fisher and modified Millard techniques for unilateral cleft lip repair.
- Comparison of Enzymatic method versus vortex and centrifugation for isolation of stromal vascular fraction from adipose tissue
- Comparison of preparation of SVF from adipose tissue by enzymatic digestion versus emulsification
- Comparison of outcome of autologus fat grafting in facial contour deformities with and without PRP
- Outcome of Type 4 saddle nose deformity using combination of dice and block cartilage
- Effect of different concentrations of adrenaline in hand surgery under tumescence anesthesia on initiation of post operative pain
- Experience of Meek grafting technique in post traumatic and post burn patients
- Effect of different concentrations of adrenaline in hand surgery under tumescence anesthesia on initiation of operative pain.
- Determination of effect of different adrenaline concentrations during intraoperative bleeding in tumescent anesthesia in wide awake hand surgery
- Outcome of facial scar appearance after autologous nanofat grafting with platelet rich plasma (PRP) versus only nanofat grafting in burn patients.
- Coverage of exposed tendons with alloderm.
- Outcome of nanofat grafting in post acne scarring.
PROJECTS / DEPARTMENTAL EXTENSION /SPECIAL FEATURES
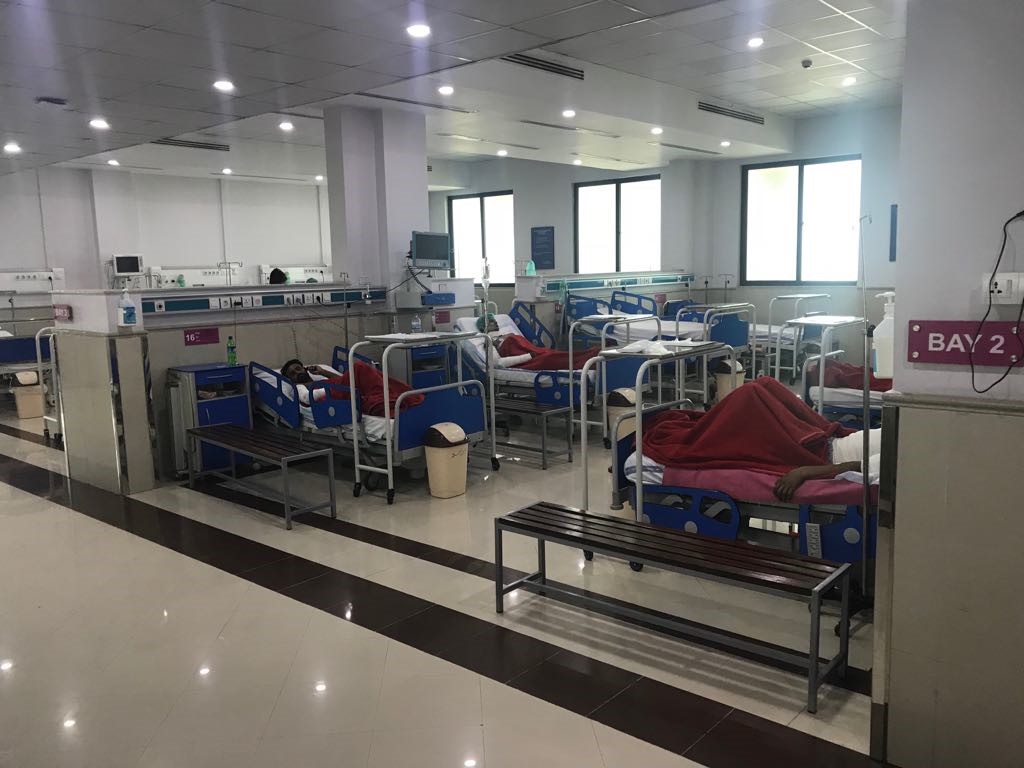
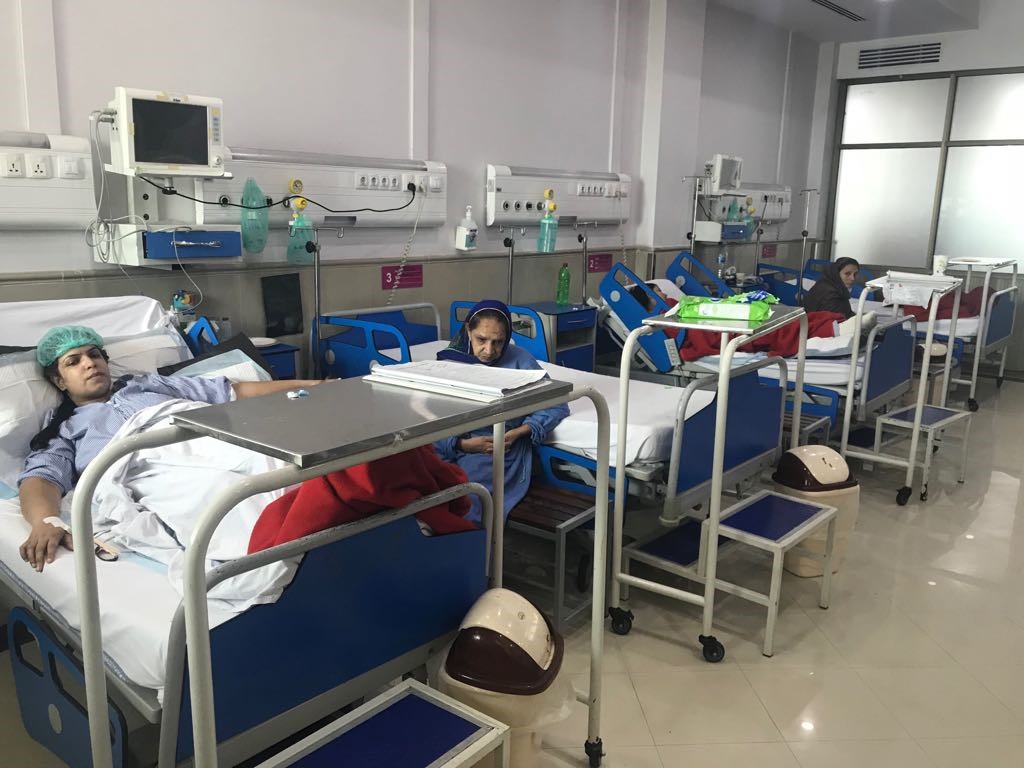
The Department of Plastic Surgery & Mayo Burn Centre is fully operational on 4th floor of Surgical Tower, Mayo Hospital, Lahore which comprises of 94 bedded state of the art facility. These 94 beds were subdivided as 30 bedded Mayo Burn Centre (largest burn centre in Punjab) and 64 bedded plastic surgery and burn reconstruction wards including 20 bedded Paediatrics Burn Reconstruction ward.
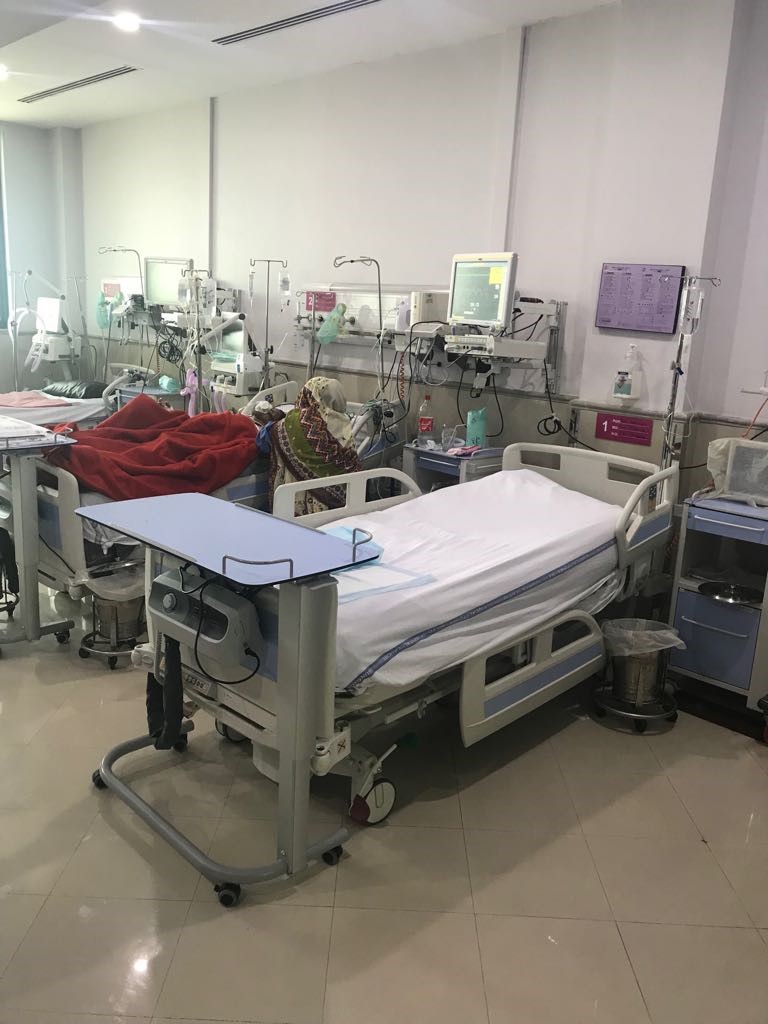
Mayo Burn Centre is fully equipped with latest gadgets which were installed in Burn ICU, HDU, Burn OT, Burn Physiotherapy and Hydrotherapy Bays. A separate burn follow-up clinic, burn operation theatre and a minor surgery operation theatre with attached sterilization facility were also the part of same floor. Burn centre also includes separate counselling/psychiatric services and rehabilitation services for burn victims. Currently on average 16320 patients present annually in the outpatient department and burn follow-up clinic. We operate on an average of 1008 cases under general anaesthesia and about 1536 cases under local anaesthesia per year.
HEALTH SERVICES / STATE OF ART FACILITIES
The department is the only facility in the country armed with state of the art equipment like:-
- Nd Yag long pulse Laser for hair removal, vascular lesions etc.
- CO2 Laser machine for Burn Scars resurfacing.
- Pulse Dye laser for heamangiomas, vascular malformations etc.
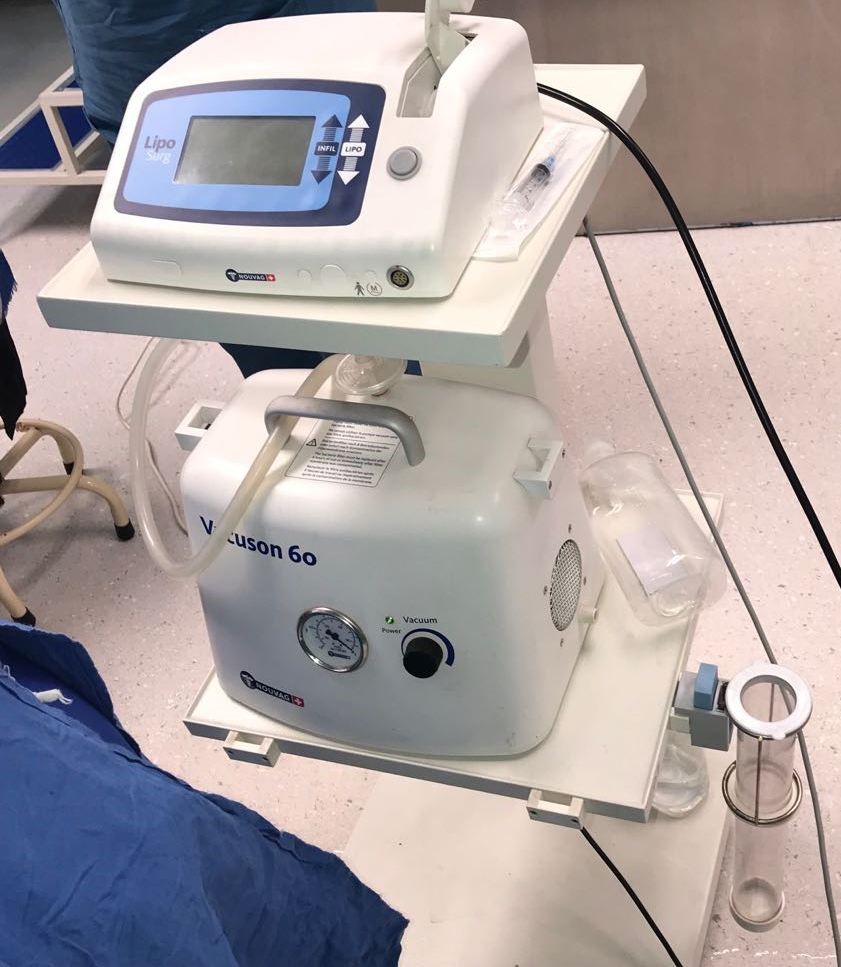
- Liposuction system for burn reconstructive purposes.
- Plastic Surgery Endoscopic unit.
- FUE hair transplant facilities for post burn alopecia reconstruction.
- Negative pressure wound healing systems (VAC).
- Air Fluidized bed for Acute burn healing.
- Laser Doppler Imaging system for burn depth assessment.
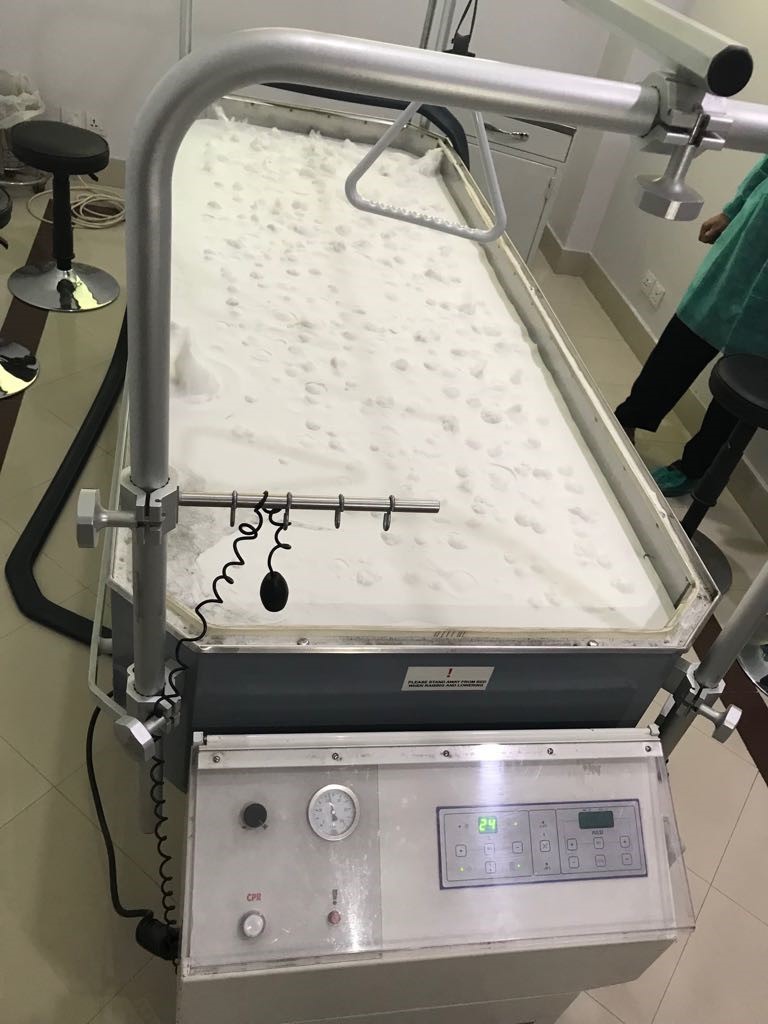
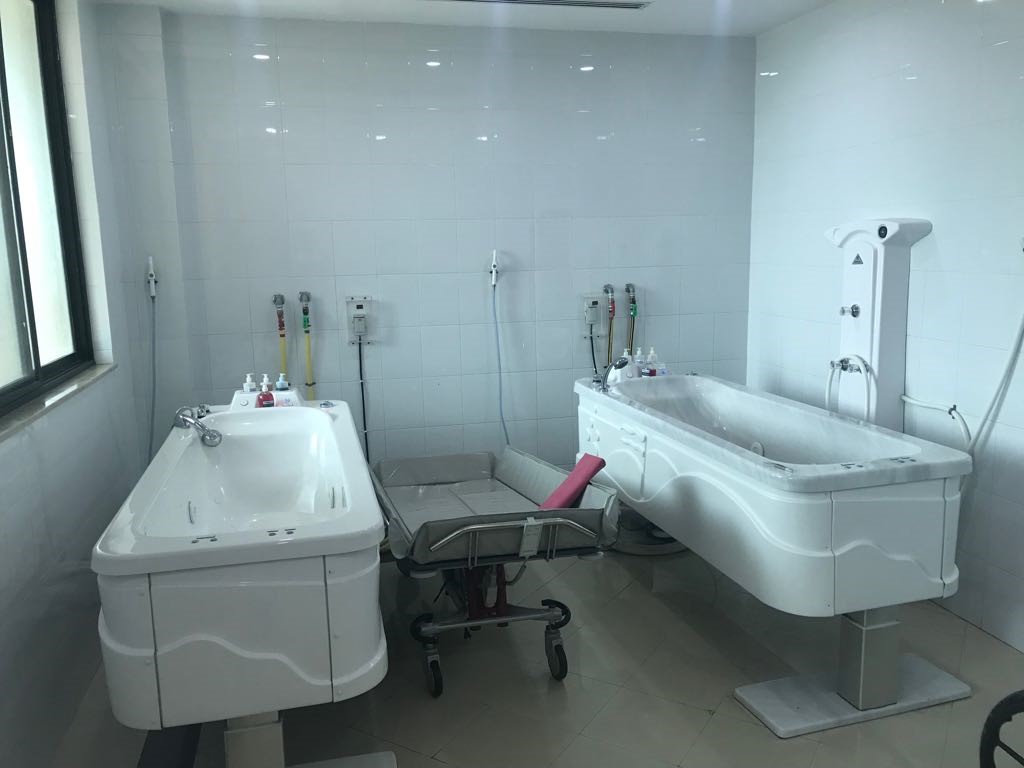
- Burn whirlpool hydrotherapy bath system and shower trolleys.
- Modern hygienic modular operation theatres.
- Anastomotic coupling device.
- High quality microscope for microsurgery.
- MEEK Skin Grafting technique.
- Since the new department is functional in surgical tower, all the data regarding patient admission and treatment is computerized and all investigation and record is IT based. Department is equipped with separate area for library and conference room in order to maximize the teaching and research facilities for residents.
- It’s not how good you are. It’s how good you want to be.
We dream and aspire to build this department into a coveted model ward and learning cradle that would inspire future generations of Plastic Surgeons.
FUTURE PLAN:
- Provision of skin bank for burn patients.
- Diagnostic lab adjacent to burn HDU.